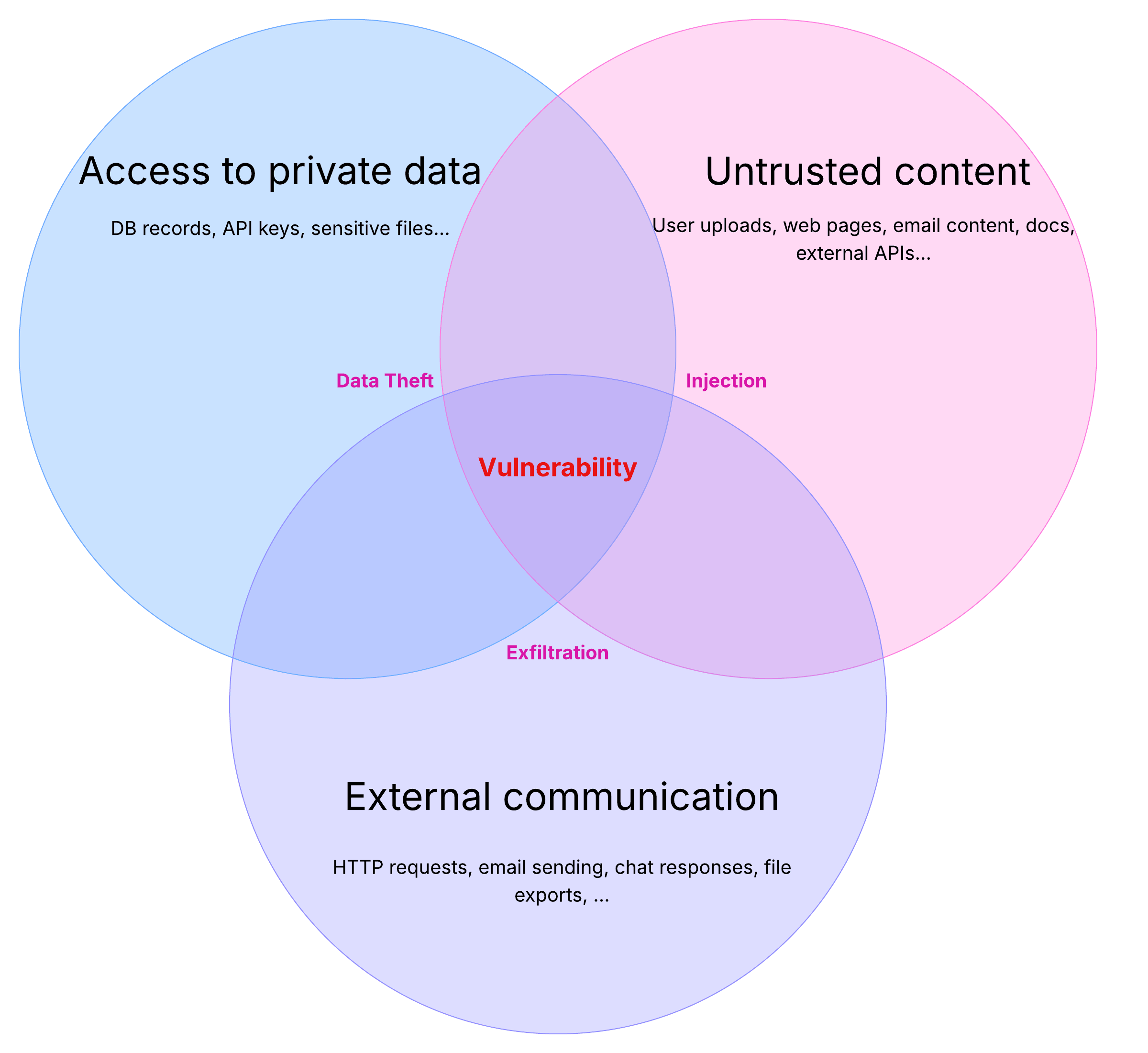
Data poisoning remains a top concern on the OWASP Top 10 for 2025. However, the scope of data poisoning has expanded since the 2023 version. Data poisoning is no longer strictly a risk during the training of Large Language Models (LLMs); it now encompasses all three stages of the LLM lifecycle: pre-training, fine-tuning, and retrieval from external sources. OWASP also highlights the risk of model poisoning from shared repositories or open-source platforms, where models may contain backdoors or embedded malware.
When exploited, data poisoning can degrade model performance, produce biased or toxic content, exploit downstream systems, or tamper with the model's generation capabilities.
Understanding how these attacks work and implementing preventative measures is crucial for developers, security engineers, and technical leaders responsible for maintaining the security and reliability of these systems. This comprehensive guide delves into the nature of data poisoning attacks and offers strategies to safeguard against these threats.