ModelAudit vs ModelScan: Comparing ML Model Security Scanners
As organizations increasingly adopt machine learning models from various sources, ensuring their security has become critical. Two tools have emerged to address this need: Promptfoo's ModelAudit and Protect AI's ModelScan.
To help security teams understand their options, we conducted a comparison using 11 test files containing documented security vulnerabilities. The setup of this comparison is entirely open-source and can be accessed on Github.
Test Methodology
Our comparison focused on real-world attack vectors commonly found in ML model supply chains:
- 5 pickle files: Including malicious code execution, encoded payloads, and one benign ML model
- 3 configuration files: Containing webhooks, exposed credentials, and executable code
- 2 archive files: With path traversal and embedded executable attacks
- 1 PMML file: For format validation testing
Each test file was scanned with both tools (ModelAudit v0.1.0 and ModelScan v0.8.5) in June 2025, with results independently verified.
Key Findings
Format Support
The tools differ significantly in the number of file formats they can analyze:
| Metric | ModelAudit | ModelScan |
|---|---|---|
| Files analyzed | 11/11 (100%) | 6/11 (55%) |
| Pickle files | 5/5 | 4/5 |
| Configuration files | 3/3 | 0/3 |
| Archive files | 2/2 | 2/2 |
| Other formats | 1/1 | 0/1 |
ModelScan focuses primarily on pickle-based formats (including PyTorch .pt/.pth files), Keras H5 files, and TensorFlow SavedModel directories. ModelAudit additionally supports configuration files (JSON, YAML, XML), ONNX models, SafeTensors, NumPy arrays, and PMML files.
Detection Capabilities
Across the 11 test files, the scanners identified different numbers of security issues:
| Metric | ModelAudit | ModelScan |
|---|---|---|
| Total issues detected | 16 | 3 |
| Files with detections | 8 | 3 |
| Average issues per malicious file | 2.0 | 1.0 |
Pickle File Analysis
Both tools successfully detected malicious pickle files. For a file containing os.system execution via __reduce__:
- ModelScan: Identified the dangerous
posix.systemreference - ModelAudit: Identified both the
REDUCEopcode and theposix.systemreference
This pattern repeated across other pickle test cases, with ModelAudit typically identifying both the execution mechanism and the dangerous function call.
Configuration Security
Only ModelAudit currently analyzes configuration files. In our test of a malicious JSON configuration file containing webhook URLs, exposed API keys, and executable code patterns, ModelAudit identified 4 distinct security issues while ModelScan could not process the file.
Archive Security
Both tools support ZIP file scanning, but with different security checks:
- Path traversal (../../../tmp/evil.sh): Detected by ModelAudit only
- Embedded executables: Detected by ModelAudit only
- Basic ZIP support: Available in both tools
Output and Integration
Both tools provide:
- Command-line interfaces
- Human-readable output
- JSON output for automation
Notable differences:
- ModelAudit includes risk scores (0.0-1.0 scale) for each finding
- ModelAudit provides security explanations for each issue
- ModelScan's JSON output may require special parsing due to embedded newlines
Use Case Considerations
ModelScan Strengths
- Focused approach to pickle-based security threats
- Lightweight implementation
- Suitable for environments primarily using pickle-based model formats
ModelAudit Strengths
- Broader format coverage across ML frameworks
- Configuration file security analysis
- More detailed vulnerability detection in supported formats
- SBOM generation capability
- Risk scoring for prioritization
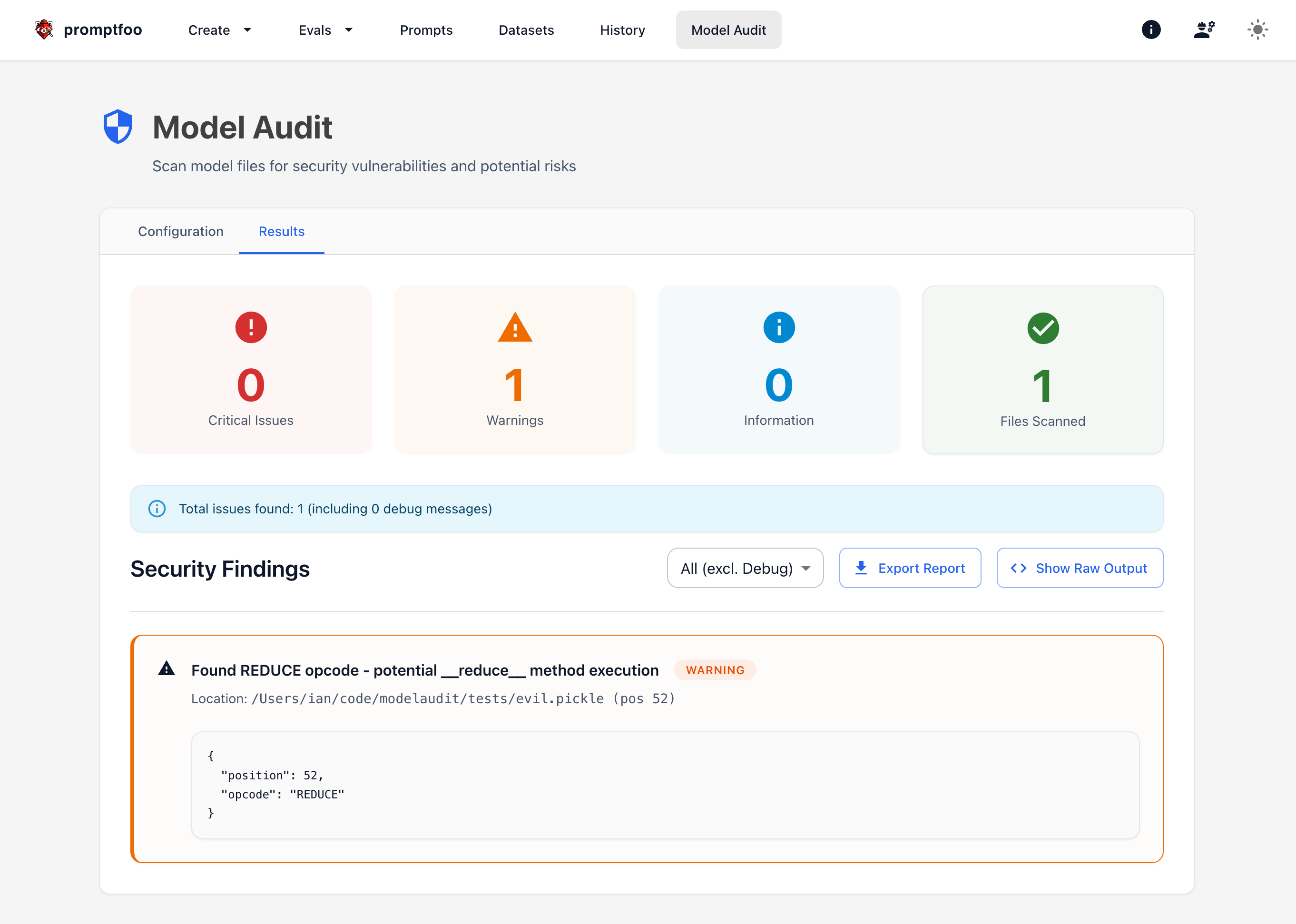
Model Audit is also not just a CLI - it comes with an optional UI via the promptfoo package:
Practical Implications
For organizations implementing ML security scanning:
-
Format diversity: Teams using multiple ML frameworks or configuration-driven pipelines may need broader format support
-
Detection depth: The difference in detection counts (16 vs 3 issues) reflects different approaches to identifying security risks
-
Integration requirements: Both tools offer CLI and JSON output suitable for CI/CD pipelines
-
Complementary use: Some organizations might benefit from using both tools for different stages of their ML pipeline
Reproducibility
All test files and comparison scripts are available on Github for independent verification:
# Generate test files
python generate_test_models.py
# Run comparison
python run_comparison_fixed.py
# View results
cat results/summary_fixed.json
Conclusion
ModelScan provides focused pickle security scanning, while ModelAudit offers broader format coverage and additional security checks. Organizations should evaluate their specific needs, including the ML frameworks they use, the types of models they deploy, and their security requirements when choosing between these tools.
The empirical data from our testing provides a baseline for comparison, but each organization's needs will vary based on their ML infrastructure and threat model. We encourage teams to test both tools with their own model formats and security requirements to make an informed decision.
Note: This comparison used ModelAudit v0.1.0 and ModelScan v0.8.5. Both tools are under active development, and capabilities may change in future versions.
