Sensitive Information Disclosure in LLMs: Privacy and Compliance in Generative AI
Imagine deploying an LLM application only to discover it's inadvertently revealing your company's internal documents, customer data, and API keys through seemingly innocent conversations. This nightmare scenario isn't hypothetical—it's a critical vulnerability that security teams must address as LLMs become deeply integrated into enterprise systems.
Unlike traditional data protection measures, sensitive information disclosure occurs when LLM applications memorize and reconstruct sensitive data through techniques that traditional security frameworks weren't designed to handle.
This article serves as a guide to preventing sensitive information disclosure, focusing on the OWASP LLM Top 10, which provides a specialized framework for addressing these specific vulnerabilities.
What is Sensitive Information Disclosure?
Let's explore the primary risks of sensitive information disclosures in LLM applications, with both real incidents and hypothetical scenarios illustrating how these risks materialize.
Risks with Foundation Models
When training a Large Language Model, the model can "memorize" data, subsequently reproducing or recalling specific portions of the training data during inference.
There are two types of memorization that can occur with an LLM:
- Verbatim Memorization: The model directly reproduces data, such as complete sentences or code snippets, from its training data.
- Semantic Memorization: The model generates outputs that convey the same meaning as training data, even if not word-for-word.
Memorization is more likely to occur when training data is frequently duplicated. Additionally, larger models with more parameters have increased capacity for memorization, as do models with larger context windows. This means that models with larger parameters and context windows are more likely to have memorized sensitive data that can be disclosed during inference.
Memorization can introduce security and privacy risks when the training data contains sensitive information, such as PII, proprietary knowledge, or customer data. Here are three scenarios where memorization can introduce risk:
-
A foundation model memorizes personal data that can be retrieved during inference.
In this scenario, a foundation model selected for enterprise deployment has been trained using sensitive personal data containing email addresses, phone numbers, and social security numbers. Although the model is trained not to disclose personal data, it memorizes these details during training. During inference, an attacker realizes they can extract this information using jailbreaks. -
A foundation model with multi-modal capabilities reproduces images that are nearly identical to a known person.
When given a prompt to generate an image, a multimodal model may reproduce an image nearly identical to one used in its training data, as demonstrated in this research example:
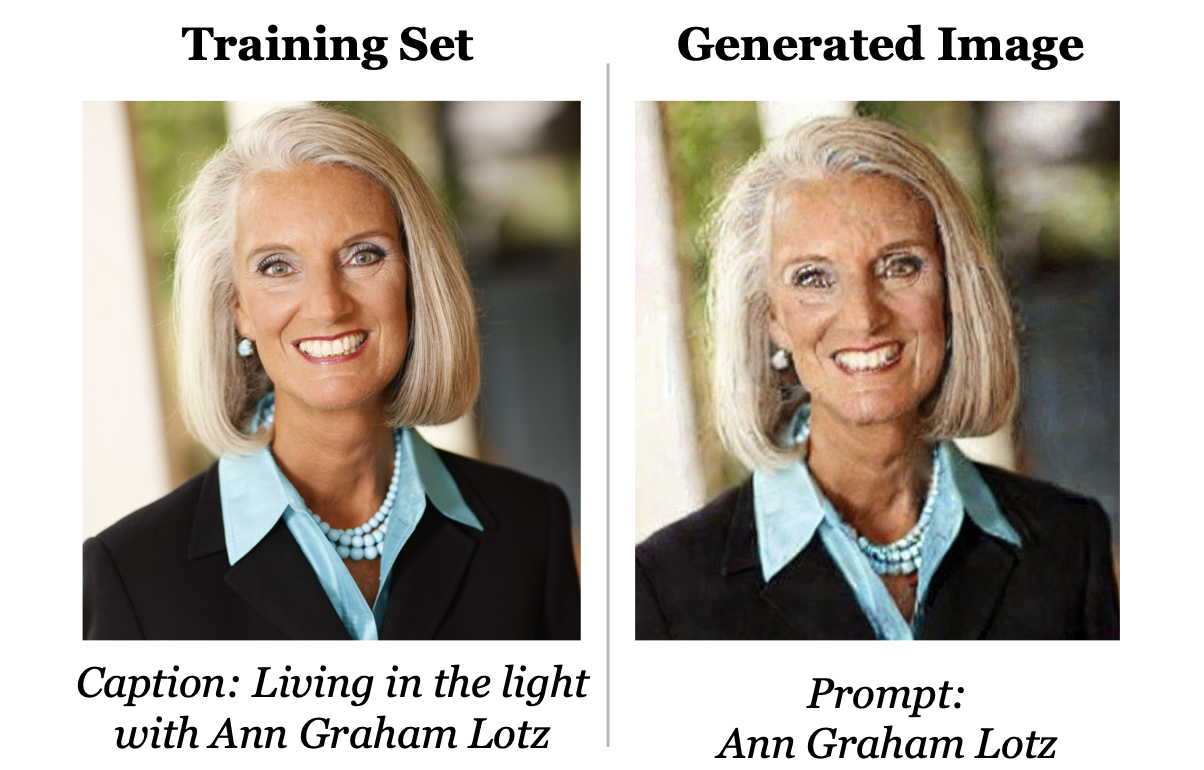
We first saw the implications of this risk in 2023 with GPT-3.5's deployment in ChatGPT. Researchers extracted a megabyte of sensitive training data by prompting the aligned model to repeat the word "poem" indefinitely, ultimately revealing email addresses and phone numbers. You can test for this vulnerability using Promptfoo's divergent repetition plugin.
Typically, LLMs deployed in production environments undergo alignment, where researchers ensure that the LLM's outputs adhere to human values, ethical standards, and organizational goals. This includes alignment that restricts a model's ability to reproduce training data that it's memorized. However, security research shows that alignment will only mitigate–and not totally eradicate–the risk of sensitive information disclosure.
Risks During Fine-Tuning
Memorization is just one risk of sensitive information disclosure. This vulnerability can also arise from process failures during fine-tuning.
If a model is fine-tuned on sensitive data that isn't properly filtered or anonymized, that data could be memorized. The risk increases without proper de-duplication, which raises the likelihood that the model will memorize and subsequently reproduce sensitive data verbatim. Without procedural controls to ensure compliance with contractual opt-out agreements, customer or user data might be inadvertently used to fine-tune a model, leading to unintentional disclosure of sensitive information.
Risk Scenario: A fine-tuned model trained on anonymized customer data discloses sensitive information.
Due to an error in the fine-tuning process, customer data isn't fully anonymized. When the model is deployed in a multi-tenant environment, other customers can potentially jailbreak the model to disclose competitors' information, such as revenue targets and product roadmaps.
Risks During Deployment
Finally, sensitive information disclosure could occur if the model is trained on sensitive information and exposed to users who otherwise would not have access to that data. Risk Scenario: A fine-tuned model memorizes proprietary information about a company.
A company wants to enhance the performance of its LLM and fine-tunes it on the company's intellectual property, such as code bases and architecture diagrams. When the model is deployed internally, employees who ordinarily wouldn't have access to sensitive, proprietary data can suddenly extract information, leading to the risk of an insider attack and IP theft.
Differences Between Sensitive Information Disclosure and Other OWASP Top 10 Risks
What makes sensitive information disclosure different from other types of vulnerabilities listed in the OWASP Top 10 for LLMs?
In many ways, sensitive information disclosure can be considered a model-layer risk. Restricted information is memorized by the model and can subsequently be regurgitated during inference. Controls such as more robust anonymization and data sanitation practices, stronger alignment, and guardrails can mitigate the risk.
This is different from leaked data from AI applications using Retrieval Augmented Generation, where sensitive data may intentionally be exposed to the LLM but the access control mechanisms may be misconfigured–subsequently leading to a data breach.
All LLMs are vulnerable to sensitive information disclosure. The risk depends on the level of exploitability based on how jailbreakable the model is and the types of controls that are in place during deployment. This risk can be amplified depending on the type of data used to fine-tune a model, the number of times the data is duplicated during training, and the general size of the model in terms of parameter and context window.
For models that are fine-tuned with restricted information, companies must also decide how the model is accessed and make informed decisions based on the principles of least privilege and need-to-know.
For instance, a large model fine-tuned on customer data that is deployed in a multi-tenant environment for a public-facing SaaS company has much higher risk than a smaller model deployed only for a small group of privileged users with robust authentication and authorization controls. A model that is trained on engineering material for an aerodefense company and exposed to all personnel–including those in HR, Finance, and Legal–has a much higher risk of sensitive information disclosure than if the model is only accessible for engineers working in R&D.
Defense in Depth Controls Against Sensitive Information Disclosure
Supply Chain Due Diligence for Third-Party Models
Conduct thorough due diligence on any models downloaded from a third-party, whether closed or open-sourced. Read model cards, conduct research on any relevant security research or CVEs, and try to understand the type of data that was used to train the model.
Exercise more caution for open-source models without model cards or those that have already been fine-tuned.
Data Sanitization for ML Teams
If your company is fine-tuning models using training data that may contain sensitive information, such as PII or customer data, then it is imperative that controls are enforced for appropriate anonymization. If you're responsible for LLM security and assessing the risks of fine-tuned or proprietary models, verify that the following controls are in place:
- Opt-Out Controls: Ensure there are technical controls to prevent the use of any data from users or companies that have opted-out of training AI models.
- Data Sanitization Techniques: Check that data sanitation procedures are in place to prevent sensitive data from being used to train models.
- Data Duplication Checks: If sensitive or proprietary data is being used, attempt to reduce data duplication, which increases the risk of memorization.
- Noise Injection: Verify to see if noise injection is in place, which is the process of modifying training data so it becomes less sensitive to minor variations in input. This will subsequently improve the LLM's performance and reduce the likelihood of verbatim or general memorization.
- Alignment: Review to see whether alignment is taking place with fine-tuned models so that the model's output meets customer and contractual expectations and does not reveal training data.
Input and Output Filtering
There are also controls that can be placed as a defense-in-depth measure when deploying models. Consider deploying guardrails that will restrict sensitive data from being sent in input or disclosed in output. This will reduce the risk of sensitive information being disclosed to end-users, even if memorization is present in the model.
Robust Access Control
Consider the type of data that has been used to train the model and apply the same data authorization to the users who will be accessing the model. For example, don't deploy a model for public use if it has been trained on proprietary information. Use the principles of least privilege and need-to-know as you would for any other corporate information.
Red Teaming the Model
Run red teams against the model or application to assess whether the model can be jailbroken to disclose sensitive information. You can achieve this in Promptfoo through several plugins:
- The PII plugin tests an AI system's ability to protect sensitive personal data.
- The harmful:privacy and harmful:intellectual-property plugins will assess whether privacy or IP violations could be exploited.
- The custom plugin can attempt to extract data from the model based on your requirements, such as attempting to pull training data on proprietary information used to fine-tune a base model.
Secure the API Itself
If you are hosting the model through an API, apply the same security controls that OWASP's API security framework recommends. Suppress debugging and logging features in API responses that may contain sensitive information and enforce robust encryption in transit.
Secure Your LLM the Right Way
Preventing sensitive information disclosure in LLMs is vital, yet it represents just one facet of a holistic approach to LLM and AI security. Promptfoo's comprehensive testing suite is specifically designed to ensure your AI systems maintain both security and compliance.
Explore Promptfoo to learn more about how you can secure your LLM applications.
